Docker & Container Security – Basic Docker Client Commands

Basic Docker Client Commands
Docker is a platform designed to help developers build, share, and run applications within containers. To interact with Docker, you’ll primarily use the Docker client via the command line interface (CLI). Below are some essential Docker commands to help you get started.
Installing Docker
Before using Docker, you need to install it. You can download Docker Desktop for Windows and macOS or Docker Engine for Linux from the official Docker website.
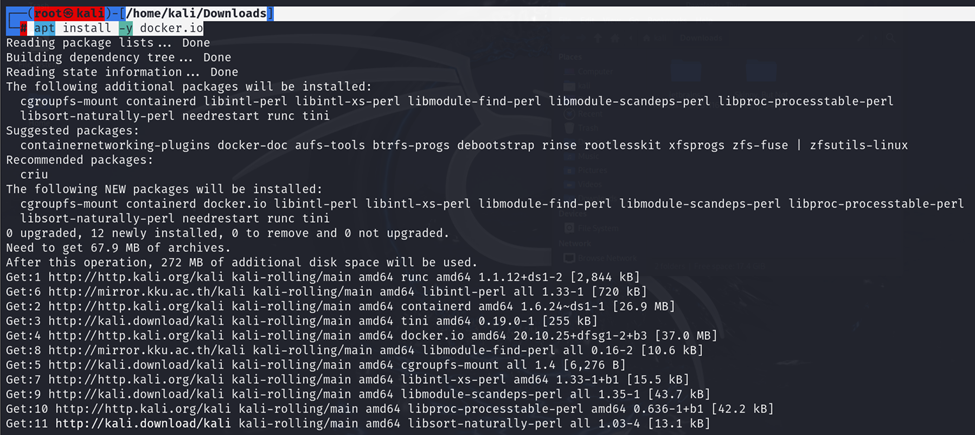
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/home/kali/Downloads]
└─# apt install -y docker.io
Starting Docker
Once installed, start Docker. On Docker Desktop, simply open the application. On Linux, you can start Docker using:

Verifying Docker Installation
To ensure Docker is installed correctly, run:

Basic Docker Commands
a. docker run
The docker run command creates and starts a new container from a specified image. For example, to run an Nginx container:

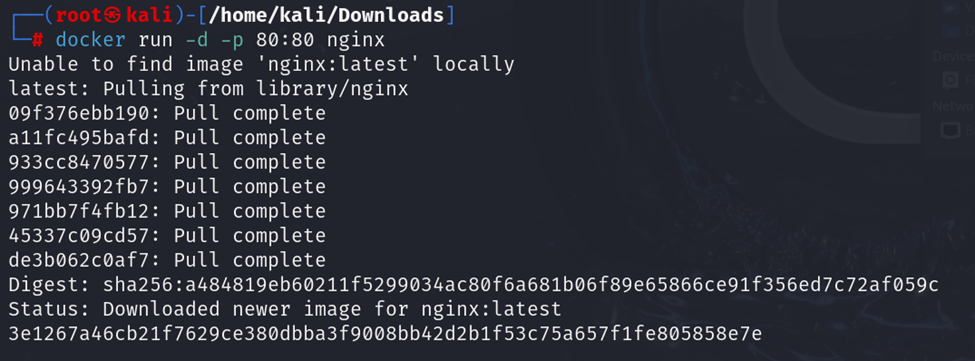
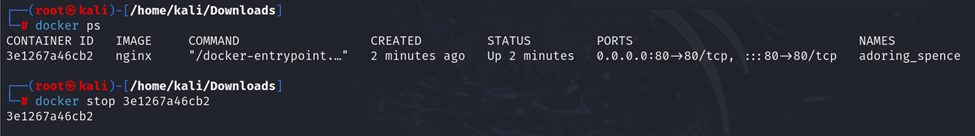
b. docker ps
To list all running containers, use:

For all containers, including stopped ones, use:

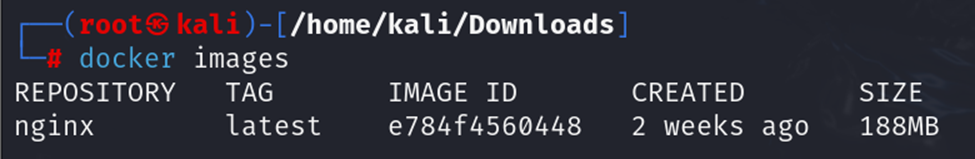
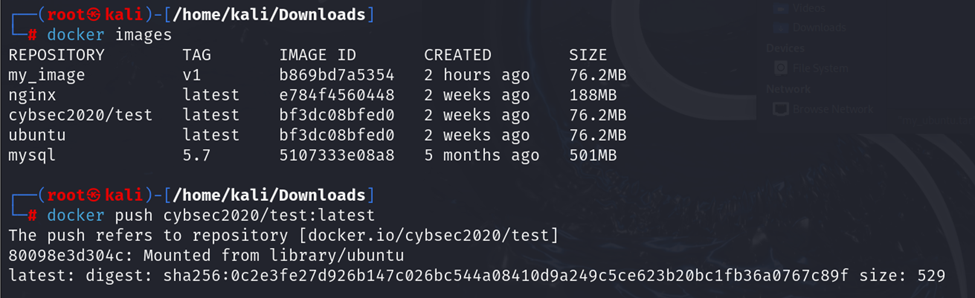
c. docker images
To list all available Docker images on your system:

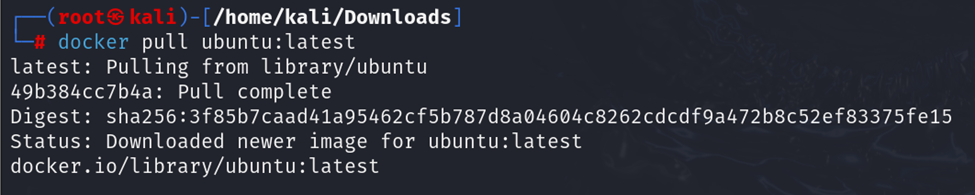
d. docker pull
To download a Docker image from Docker Hub, use:

For example, to pull the latest Ubuntu image:

e. docker stop
To stop a running container, use:

You can find the container ID using the docker ps command.
f. docker rm
To remove a stopped container, use:

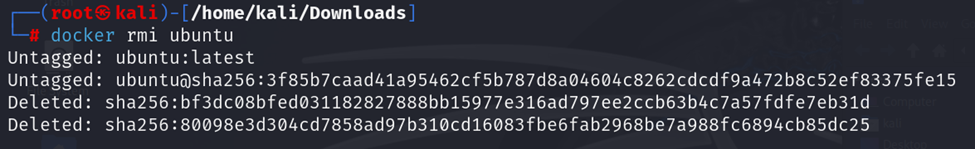
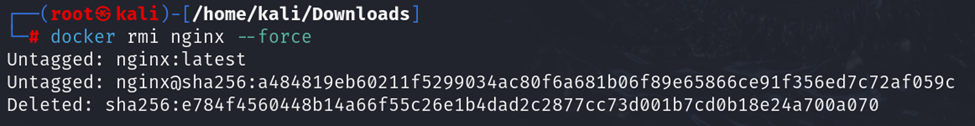
g. docker rmi
To remove a Docker image, use:

docker start
The docker start command is used to start one or more stopped containers.
Syntax:

Example:

docker push
The docker push command uploads an image to a Docker registry.
Syntax:

Example:

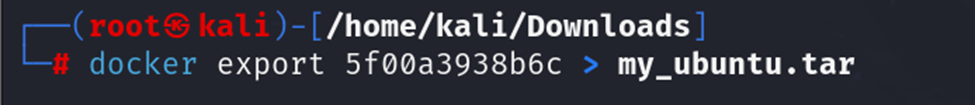
docker export
The docker export command is used to export a container’s filesystem as a tar archive.
Syntax:

Example:

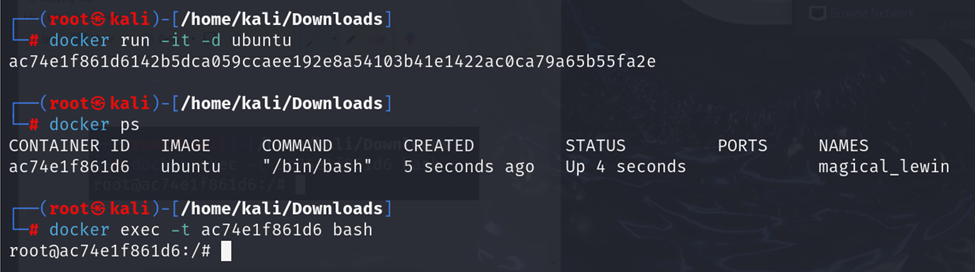
docker exec
The docker exec command runs a new command in a running container.
Syntax:

Example:

-itruns in interactive mode with a TTY (useful for opening a shell).
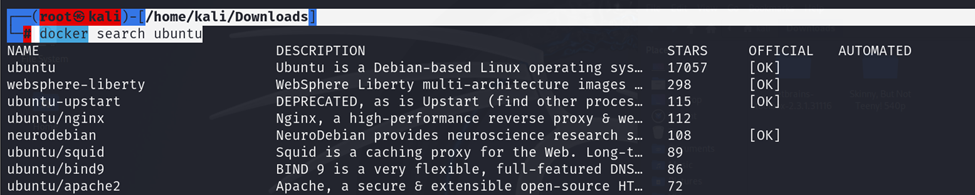
docker search
The docker search command searches for images on Docker Hub.
Syntax:

Example:

┌──(root㉿kali)-[/home/kali/Downloads]
└─# docker search Ubuntu
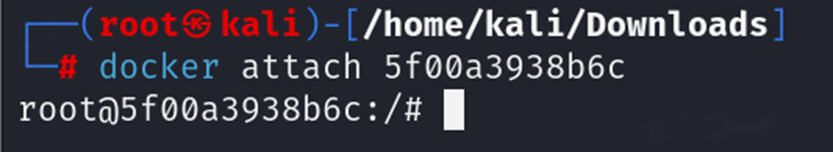
docker attach
The docker attach command attaches your terminal to a running container.
Syntax:

Example:

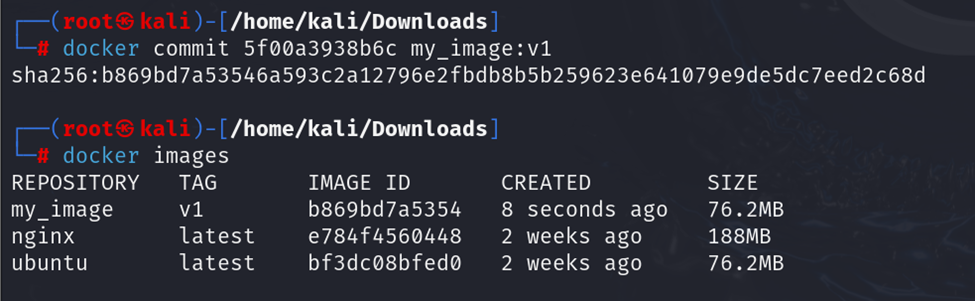
docker commit
The docker commit command creates a new image from a container’s changes.
Syntax:

Example:

Managing Docker Containers
a. Inspecting Containers
To view detailed information about a container:

b. Viewing Logs
To view the logs of a container:

c. Executing Commands Inside a Container
To run a command inside a running container:

For example, to open a bash shell inside a container:

Docker Compose
Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. To install Docker Compose, follow the instructions on the official Docker Compose installation page.
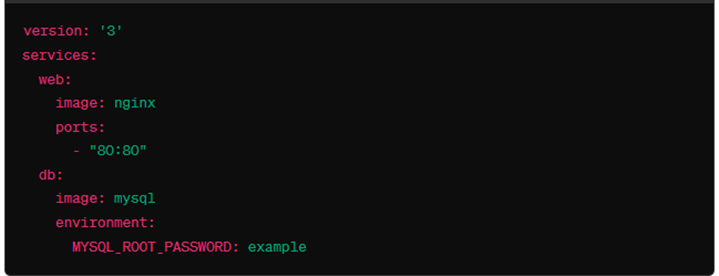
To start the services defined in the docker-compose.yml file, run:

Conclusion
These basic Docker commands will help you get started with managing containers on your development environment.
@SAKSHAM DIXIT
