Docker & Container Security – Building a Blue Teaming Lab with Docker and Containers

Building a Blue Teaming Lab with Docker and Containers
Building a Blue Teaming lab using Docker and containers can provide security professionals with a controlled environment to practice defensive security techniques, monitor and analyze network traffic, and develop incident response skills. Below is a guide to building a Blue Teaming lab using Docker.
- Choose Docker Host:
- Select a suitable host system (physical or virtual) to run Docker. Ensure it has sufficient resources like CPU, memory, and disk space to support multiple containers.
- Install Docker:
- Install Docker CE (Community Edition) on the chosen host system.
- On Linux:
- Install Docker CE (Community Edition) on the chosen host system.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
- On Windows or macOS: Download and install Docker Desktop from the official Docker website.
- Pull Docker Images:
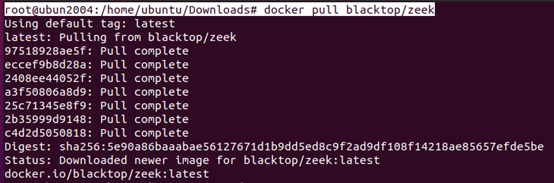
- Pull Docker images for Blue Teaming tools and security monitoring solutions you want to use. You can find these images on Docker Hub or other container registries.
root@ubun2004:/home/ubuntu/Downloads# docker pull blacktop/zeek
- Create Docker Network:
- Create a Docker network to facilitate communication between containers.
docker network create blueteam
- Run Docker Containers:
- Run Docker containers for different Blue Teaming tools and components, ensuring they are connected to the same Docker network.
docker run –name <container_name> –network blueteam -d <image_name>
- Configure Container Interaction:
- Set up port forwarding or publish container ports to interact with Blue Teaming tools running inside containers.
docker run –name <container_name> –network blueteam -p <host_port>:<container_port> -d <image_name>
- Customize Containers:
- Customize Docker containers as needed by modifying configuration files, installing additional packages, or building custom images from Dockerfiles.
- Simulate Network Environment:
- Set up simulated network environments using Docker containers to mimic real-world scenarios, including internal networks, DMZs, and client-server architectures.
- Deploy Security Monitoring Solutions:
- Deploy security monitoring solutions such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection/Prevention System), and packet capture tools inside Docker containers.
- Implement Security Controls:
- Configure security controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection rules, and access control policies within Docker containers to defend against simulated attacks.
- Practice Incident Response:
- Create and simulate security incidents within the Blue Teaming lab environment to practice incident detection, analysis, and response procedures.
- Monitor and Analyze Traffic:
- Monitor network traffic and system logs generated by Docker containers using Blue Teaming tools to identify potential security issues and anomalies.
- Document and Maintain:
- Document the setup and configurations of the Blue Teaming lab for future reference.
- Regularly update and maintain the lab environment to incorporate new tools, patches, and security enhancements.
Security Monitoring and Analysis:
- Security Onion (https://github.com/security-onion-solutions/security-onion/wiki/Docker):** A preconfigured Linux distribution offering a comprehensive suite of open-source security tools like Suricata (IDS), Bro (network traffic analysis), Wireshark (packet capture), and Maltego (link analysis). It’s ideal for centralized security monitoring and analysis.
- OSSEC (https://hub.docker.com/r/atomicorp/ossec-docker/):** Open Source Security Event Correlation (OSSEC) is a Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) that monitors system logs, files, registry keys, and processes for suspicious activity.
- Zeek (https://hub.docker.com/r/blacktop/zeek):** Formerly known as Bro, Zeek is a powerful network traffic analyzer that can be used for real-time network security monitoring and forensic analysis.
Log Management and Analysis:
- ELK Stack (https://hub.docker.com/_/elasticsearch):** The Elastic Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana) offers a popular platform for log collection, storage, analysis, and visualization. It allows blue teamers to analyze logs from various security devices, applications, and systems to identify anomalies and investigate incidents.
- Graylog (https://hub.docker.com/r/graylog/graylog/):** Similar to ELK Stack, Graylog is another open-source log management platform that provides centralized log collection, storage, searching, and alerting for security purposes.
Digital Forensics and Incident Response:
- ForensicToolkit (https://github.com/docker-forensics-toolkit/toolkit):** This image includes a collection of open-source forensic tools like Autopsy (forensic analysis platform) and Volatility (memory forensics framework). It allows blue teamers to investigate security incidents, collect evidence from compromised systems, and perform forensic analysis.
- Sans DFIR (https://www.sans.org/webcasts/docker-crash-course-containerize-your-favorite-security-tools/):** This image provides a pre-configured environment with various tools for digital forensics and incident response (DFIR) activities, including SANS utilities and other open-source tools.
Active Directory Security:
- BloodHound (https://github.com/belane/docker-bloodhound):** This graph visualization tool helps visualize relationships between Active Directory objects (users, groups, computers). Blue teamers can leverage it to understand how attackers might move laterally within a network after gaining initial access.
Additional Considerations:
- Data Persistence: Decide on a strategy for storing and managing security data generated within the lab. Utilize Docker volumes for persistent data storage within containers.
- Security Monitoring: Integrate tools for monitoring container health and security metrics to identify potential issues within the lab environment itself.
Here are some resources for blue teaming labs with Docker:
- Blue Team Dojo: https://www.sans.org/job-roles-roadmap/cyber-defense/ (While not Docker-specific, offers valuable insights for building a blue team lab)
- Security Onion: https://securityonionsolutions.com/ (Security-focused Linux distribution that can be containerized)
- OSSEC Docker Image: https://hub.docker.com/r/atomicorp/ossec-docker/ (Open Source Security Event Correlation)
Remember:
- Ethical Usage: Use your blue teaming lab for educational purposes or authorized security testing with proper permissions.
- Realistic Scenarios: Strive to design scenarios that reflect real-world security threats and challenges for effective training.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly update the lab with new security tools, scenarios, and attack techniques to maintain its relevance and effectiveness.
@SAKSHAM DIXIT