Docker & Container Security – Building a Red Teaming Lab with Docker and Containers

Building a Red Teaming Lab with Docker and Containers
Building a Red Teaming lab using Docker and containers can provide a flexible and scalable environment for conducting security assessments and simulations. Here’s a step-by-step guide to set up a Red Teaming lab using Docker:
- Choose Docker Host:
- Select a suitable host system (physical or virtual) to run Docker. Ensure it has sufficient resources like CPU, memory, and disk space to support multiple containers.
- Install Docker:
- Install Docker CE (Community Edition) on the chosen host system.
- On Linux:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
- On Windows or macOS: Download and install Docker Desktop from the official Docker website.
- Pull Docker Images:
- Pull Docker images for various Red Teaming tools you want to use. You can find these images on Docker Hub or other container registries.
root@ubun2004:/home/ubuntu/Downloads# docker pull xer0dayz/sn1per
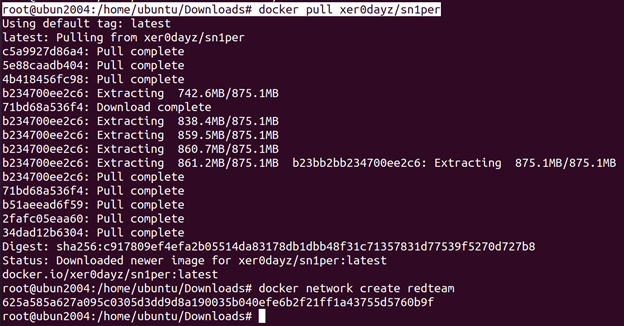
- Create Docker Network:
- Create a Docker network to facilitate communication between containers.
root@ubun2004:/home/ubuntu/Downloads# docker network create redteam

- Run Docker Containers:
- Run Docker containers for different Red Teaming tools, ensuring they are connected to the same Docker network.
root@ubun2004:/home/ubuntu/Downloads# docker run –name sn1per –network redteam -d 7e6cbb524df9

- Run the Container:
root@ubun2004:/home/ubuntu/Downloads# docker run -it 7e6cbb524df9 /bin/bash
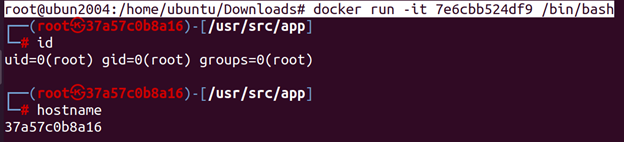
- Customize Containers:
- Customize Docker containers as needed by modifying configuration files, installing additional packages, or building custom images from Dockerfiles.
- Connect Containers:
- Set up communication channels between containers to simulate real-world scenarios, such as setting up C2 (Command and Control) infrastructure.
- Configure Host Firewall:
- Adjust host firewall settings to control inbound and outbound traffic to Docker containers, ensuring isolation and security.
- Implement Security Measures:
- Apply security best practices to Docker containers, such as limiting resource usage, using non-root users, and applying Seccomp or AppArmor profiles.
- Test Lab Environment:
- Validate the functionality of the Red Teaming lab by conducting tests and simulations, ensuring all components interact as expected.
- Document and Maintain:Document the setup and configurations of the Red Teaming lab for future reference.
- Regularly update and maintain the lab environment to incorporate new tools, patches, and security enhancements.
Additional Considerations:
- Vulnerable Applications: Include vulnerable applications in your lab environment to practice exploitation techniques. Some Docker images contain pre-configured vulnerable apps.
- Security Tools: Integrate security tools like honeypots into your lab to simulate real-world security defenses and detect potential attacks.
Here are some additional resources to get you started:
- Redcloud: https://github.com/RedTeamOperations/RedCloud-OS (Automated Red Team Infrastructure deployment using Docker)
- Docker Documentation: https://docs.docker.com/
- Docker Compose: https://docs.docker.com/compose/
Remember:
- Ethical Hacking: Only use your red teaming lab for authorized testing on permitted systems.
- Security Measures: Implement security measures within your lab environment to prevent accidental compromise of external systems.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated on emerging red teaming techniques and tools to maintain a valuable and realistic lab environment.
By following these steps, you can create a robust Red Teaming lab using Docker and containers, enabling you to conduct security assessments, penetration tests, and Red Team operations effectively.
@SAKSHAM DIXIT
